The complete monitoring experience for your phone
Get XNSPY and start tracking calls, texts, multimedia, locations and more on any phone!
Get Started Now Live DemoIntroduction to Catfishing
The prevalence of online dating in techno sexual era is met with instant gratification by the users as the gap between physical and digital dating is reduced. Though online dating is hardly original but there are more than 40 million people looking out for love via social networking sites. Apart from being gamified, the process of dating has been sexualized, thanks to digital technology. There are hardly any realistic profiles when dating online, yet the level of attractiveness is much more in online hook-ups than actual hook-ups.
However, pervasiveness of evil attached to online relationships cannot be ignored. Whether out of boredom, curiosity, revenge, or loneliness, there’s an emerging class of scam artists out there, paving their way into romantic or work relationships with unsuspecting victims being tricked for love or job, respectively. These online predators fabricate their identity to spark up an online relationship with the target. By creating fake profiles, the scammers provide a window into how the victims should see them and how far they fall from reaching those ideals. Such social schemes have drastic effects on the lives of the victims.
Many potential victims often come up with questions like, ‘Why does he prefer to chat instead of using a webcam?’ or, ‘Why does she seem too good to be true?’. Rather than being intrigued, such queries can be brought to light so that everyone can be aware of the scammers. After the release of the documentary, the word ‘Catfish’ has officially been canonized into the English dictionary.
what are the most common tactics used by catfishers
the most common tactics used by catfishers include:
1. Building Trust: Catfishers create a false online persona designed to appeal to their victim’s desires and interests. They use fake social media profiles and photos to add credibility to their persona and build trust over time. [1]
2. Emotional Manipulation: Once trust is established, catfishers will begin to manipulate their victim’s emotions. They may use guilt, fear, or sympathy to control the victim’s actions, such as asking for money or other forms of support. [1]
3. Gaslighting: Catfishers may deny or alter facts to make their victims question their own sanity and memories. This tactic is used to maintain control over the victim. [1]
4. Love Bombing: Catfishers will shower their victims with excessive attention, affection, and promises of a future together to create a false sense of intimacy and attachment. [1][3]
5. Identity Theft: In some cases, catfishers may go as far as stealing a victim’s personal information to open credit cards or take out loans in the victim’s name, causing significant financial damage. [1]
6. Exploiting the Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Catfishers may create a sense of urgency or scarcity to push their victims into making impulsive decisions or overbidding. [1]
7. Strategic Anchoring: Catfishers may set high initial bids or prices to influence the victim’s perception of value and lead them to bid higher than intended. [1]
These psychological manipulation tactics allow catfishers to deceive and exploit their victims, often with significant emotional and financial consequences. Awareness of these tactics is crucial to avoid falling victim to catfishing scams. [2][3][4]
Citations:
[1] https://fastercapital.com/topics/the-psychological-tactics-used-by-catfishers.html
[2] https://www.avast.com/c-catfishing-signs
[3] https://fastercapital.com/content/Social-Engineering–Catfishers-and-the-Art-of-Manipulation.html
[4] https://facia.ai/blog/catfishing-meaning-7-cybersecurity-tips-history-and-examples/
[5] https://www.burnettfoundation.org.nz/articles/culture/touching-tips-clocking-catfish-before-they-catch-you/
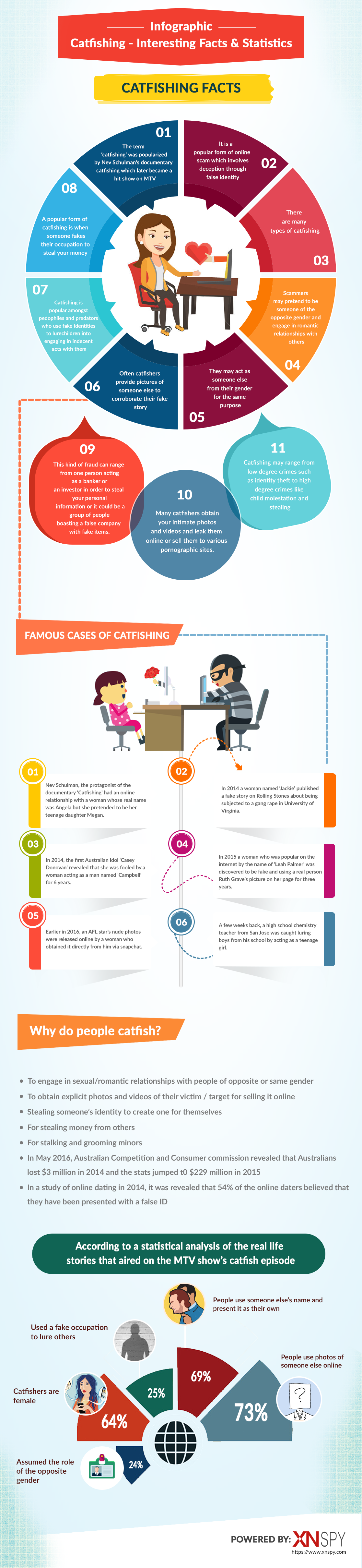
Catfishing statistics
Catfishing statistics provide valuable insights into the prevalence and impact of this deceptive online practice. Here are some key statistics:
1. Prevalence:
– 13% of American adults have reported being catfished[2].
– 20,000 people are targeted by catfishers annually in the United States[2].
2. Financial Impact:
– The global financial cost of catfishing hit $600 million in one year[2].
– The average quarterly loss of all catfishing attacks in the US stands at $132.5 million[1].
– Victims lose an average of $2,500 to catfish scams[3].
3. Platforms Used:
– 21% of all victims of catfishing met their perpetrator on Facebook[2].
– 17% experienced it from Instagram, while 15% are from Twitter[2].
– 68% of all catfishing victims met a person using a fake identity through dating sites and apps[2].
4. Country-Wide Statistics:
– The Philippines had the highest number of reported catfishing incidents, with £2,506 average loss per victim[2].
– The United Kingdom had the highest cost of romance-related catfishing incidents, amounting to £24 million[2].
5. Victim Demographics:
– Women are 50% more likely than men to be targeted by catfishers[3].
– 41% of catfish victims are between the ages of 18-34[3].
– The average age of a catfish scam victim is 50 years old[3].
6. Reporting and Resolution:
– Only 20% of catfish victims report the incident to authorities[3].
– Over 70% of catfish cases are unresolved due to anonymity protection laws[3].
7. State-by-State Data:
– Alaska has the highest number of catfished victims per capita, at 11.5[4].
– Residents of Alaska lost $1 million in a single year to catfishing[4].
These statistics highlight the widespread nature of catfishing and its significant financial and emotional impact on victims.
Citations:
[1] https://www.idstrong.com/sentinel/8-internet-catfishing-statistics/
[2] https://earthweb.com/internet-catfishing-statistics/
[3] https://wifitalents.com/statistic/social-media-catfish/
[4] https://bestvpn.org/catfishing-statistics/
[5] https://allaboutcookies.org/catfishing-scams-by-state
how can I protect myself from being catfished
To protect yourself from being catfished, follow these steps:
1. Be Suspicious:
– Be cautious of messages from people you don’t know.
– If someone messages you privately, ask them questions that only someone with their background would know. If they’re hesitant or slow to answer, be wary[1][2][4].
2. Don’t Fall Too Quickly:
– Take your time to get to know someone. Don’t rush into anything.
– Use reverse-image search to verify the person’s identity[1][2][4].
3. Take It Slow:
– Build a relationship gradually. Don’t let emotions cloud your judgment.
– Ask questions about their background and verify the information[1][2][4].
4. Talk to Someone You Trust:
– Share your concerns with a trusted friend or family member.
– Get a second opinion to help you make informed decisions[1][2][4].
5. Never Send Them Anything:
– Don’t send money, personal information, or gifts to someone you don’t know well.
– Be cautious of requests for financial help or personal data[1][2][4].
6. Use Reverse Image Search:
– Verify the identity of people you meet online by using reverse-image search tools.
– This can help you detect fake profiles and catfishers[2][4].
7. Know the Signs:
– Be aware of common catfishing tactics, such as low social media engagement, inconsistent stories, and requests for money[1][2][3].
8. Protect Your Reputation:
– Educate yourself and others about catfishing and its consequences.
– Use cybersecurity measures to protect your devices and online presence[3][4].
9. Report Suspicious Activity:
– If you suspect someone is catfishing you, report them to the platform where you met and to local authorities[1][2][4].
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of being catfished and protect your online safety.
Conclusion
The catfisher effect: the psychology of catfishing is that they gain satisfaction from the fact that they have complete control over the way their targets perceive them. No matter how closely you scrutinize things at your end, you cannot guarantee whether a person interested in you is a catfisher or not. To determine the truth, you can consider resorting to cellphone spy apps in order to reveal the true identity of the person befriending you.
Apart from the cases discussed above, there are so many men and women attacked by scammers every day. You can’t keep calm when catfishers are all around you and your loved ones. You need to be concerned whether it’s your work or personal life. Catfishers can scam your kids, spouses or employees so you need to keep a watch over them so that if anything unusual is going on, you can rectify it beforehand. Therefore, digital technology like spying apps is apt for the purpose.
By installing monitoring apps like XNSPY, you can keep a tab on a person’s calls and texts and also learn about their social media activities by monitoring all their social networking accounts. The way they carry out their chat conversations with different people can reveal a lot about their gender and their purpose for pursuing you. Also, if they’re not willing to meet you, you can always find out where they currently are, by tracking their location and catch them off-guard. This will immensely help you if you proceed for another online relationship.


